SIMP 6.4+: The ISO installation/Puppetfile workflow
Add your comments directly to the page. Include links to any relevant research, data, or feedback.
This log updates an earlier decision
This decision refines decisions from the log, How to restructure the RPM installation sequence to be more r10k/Code Manager friendly.
This document describes proposed behavior in an upcoming SIMP release (6.4.0+). Links to SIMP's documentation refer to the current release of SIMP at the time of writing (6.3.3).
Table of Contents
Background
This article describes the workflow specific to installing a fresh SIMP 6.4.0+ server from an ISO. It builds on the decision log SIMP 6.4.0: What r10k-friendly RPM features should it include?.
Drivers:
- SIMP 6.4.0 will begin to treat the r10k/Code Manager workflow as a first-class citizen.
- Puppet modules are distributed as RPMs, signed by a known GPG key as part of SIMP's implementation of NIST 800.53, CM-7(5).
- Modern Puppet module management practices use git and r10k, a model that does not fit well with RPM-distribution.
Other considerations:
- Installation by ISO is intended to be an easy way to get started, and ensure that all files are present (including Puppet modules).
- SIMP supports installations in offline/network-isolated enclaves.
Relevant data
What the word "Environment" means
The term "environment" is heavily overloaded with respect to SIMP, Puppet, DevOps, and IT in general.
This decision log uses the SIMP-specific terminology defined in the design article, SIMP Environments.
Proposed workflow
High-level workflow
For reference, the process has been broken down into stages A, B, and C:
A: (Admin) installs SIMP from ISO
(Admin) installs SIMP from ISO, ala the SIMP docs procedure, "ISO Installation (preferred)."
- (A1) The OS and RPMs are installed according to the ISO's
auto.cfg. - (A2) The post-installation of each Puppet module RPM will create an associated local bare git repository, with a tagged commit for the module's current version.
- This is option 1 of SIMP 6.4.0: What r10k-friendly RPM features should it include?)
- (A3) The rest of the SIMP ISO installation proceeds normally.
Key 6.4.0+ differences:
- At the end of the ISO installation:
- All puppet modules have a local bare git repo, with a tagged commit
- There is no
simpPuppet environment yet,/etc/puppetlabs/code/environments/simp - There is no /var/simp/environments/simp yet
B: Admin runs simp config
(Admin) logs into the newly-installed SIMP host and runs simp config.
- At an early stage (before applying with the standard action items from the questionnaire):
- (B1) Logic determines if it needs to create the first Puppet environment directory and auto-deploy the SIMP Puppet Modules
- This will always be "yes" after a fresh ISO install
- (B2) (If yes:) Auto-deploy the first Puppet environment + modules
- Details are in the "auto-deploy" section.
- (B1) Logic determines if it needs to create the first Puppet environment directory and auto-deploy the SIMP Puppet Modules
Key 6.4.0+ differences:
All stage B logic is new to simp config, and it replaces RPM logic in SIMP ≤ 6.3. Specifically, it replaces the old logic between simp-environment and simp-adapter that effectively accomplished the "auto-deploy" in SIMP ≤ 6.3, but in an opinionated manner that can conflict with r10k administration. The old logic:
- created the
simp/Puppet environment directory, and - auto-deployed each RPM-installed Puppet module's files into the
simpPuppet environment usingrsync.
By contrast, the new logic will:
- ensure that a
productionenvironment exists under the Puppet (/etc/puppetlabs) and Secondary (/var/simp/...) environment directories, while runningsimp config.- Note that this is now the
production/ environment—with r10k workflows, it doesn't make sense to create asimp/ symlinked toproduction/
- Note that this is now the
- create an initial
PuppetfileandPuppetfile.simpin theproductionPuppet environment directory - deploy the new
Puppetfileusingr10k puppetfile install
A significant difference is that the simp config "auto-deploy" only runs once in the lifetime of the the SIMP server, whereas the SIMP ≤ 6.3 the auto-deploy executed during the %post or %posttrans of each Puppet Module and simp-environment RPM, including upgrades.
- The initial Puppet environment in SIMP ≤ 6.3 was created upon the installation of the
simp-environmentRPM.- There is only one circumstance when SIMP 6.4+ will auto-generate a Puppet environment, and that is when
simp configis run on a Puppet server without any deployed Puppet environments. - In practice, this means that all later environments must be created by the administrator—never automatically.
- There is only one circumstance when SIMP 6.4+ will auto-generate a Puppet environment, and that is when
- The Puppet module auto-deploy logic in SIMP ≤ 6.3 executed immediately upon the installation of every RPM, which happened during and after the initial SIMP ISO installation.
- There is only one circumstance when SIMP 6.4+ will auto-deploy Puppet modules, and that is when
simp configis run on a Puppet server without any deployed Puppet modules. - In practice, this means that all later deployments must be initiated by the administrator—never automatically.
- There is only one circumstance when SIMP 6.4+ will auto-deploy Puppet modules, and that is when
C: Remainder of SIMP installation process
After deploying the initial Puppet environment, the rest of the SIMP installation continues without any specific alterations to support the Puppetfile-based workflow. This includes the remainder of simp config (C1), (admin-initiated) simp bootstrap, (admin-initiated) reboot, and the post-boot Puppet agent run.
Workflow details
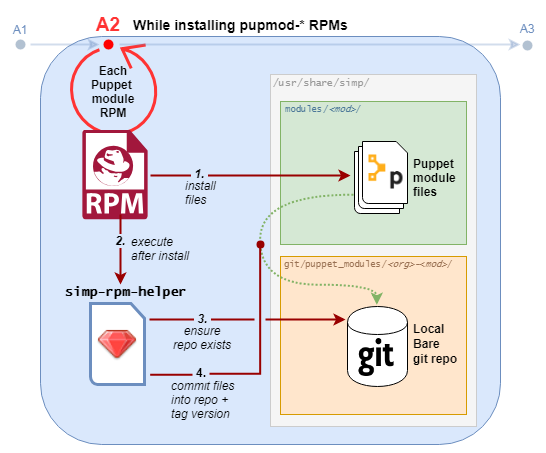
A2: Puppet module RPMs + local bare git repositories
- After a SIMP-packaged Puppet module RPM is installed, the system's
simp_rpm_helperscript ensures that a local bare git repository exists for the module, and it contains a commit of the modules files (tagged with the module's version). - This is a prerequisite for
simp puppetfile generateto work. - A prototype for this workflow was already implemented during SIMP-6083.
B2: simp config's initial "auto-deploy"
The "auto-deploy" referenced in stage B2 must perform at least three actions:
- Create the
productionPuppet environment directory$codedir/environments/productionand secondary environment directory at/var/simp/environments/.production- There is currently no logic to do this.
- A manual command has been proposed during architecture discussions, currently referred to as
simp environment new ENVIRONMENT(see section below).
- Generate the
PuppetfileandPuppetfile.simpin the Puppet environment directory.
(As of SIMP-6193) this can currently be accomplished manually by running:simp puppetfile generate --skeleton > Puppetfilesimp puppetfile generate > Puppetfile.simp
- Deploy the SIMP Puppet modules
- This can be done by running
r10k puppetfile installafter thePuppetfileandPuppetfile.simpare in place.
- This can be done by running
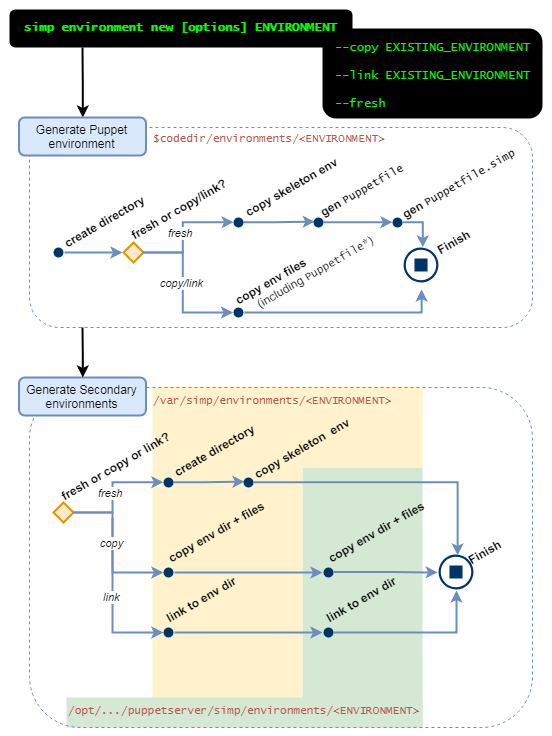
B2: simp environment new ENVIRONMENT
During the initial planning for the ISO installation, it was noted that the initial install (and subsequent admin work) would need to create environments.
Deployment scenarios
This proposed ISO+Puppetfile workflow accommodates all common Puppetfile-based deployment methods as natively as possible.
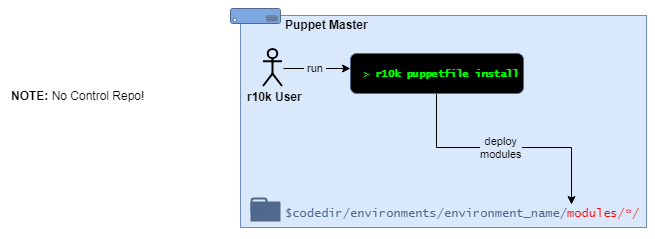
ISO-only: r10k + RPM-delivered module repositories
Local Puppet admin(s):
- deploy Puppet modules from an existing Puppet environment directory
- use the command
r10k puppetfile installto deploy the modules defined in the localPuppetfile. - the module repos can be git repositories on the local filesystem, referenced via
file://urls.
6.4.0+: The new ISO+Puppetfile workflow is most relevant to this scenario.
- It automatically provides local git repositories for each module, and a tool to update the
Puppetfile.simp. - It works immediately after installing SIMP from an ISO in any environment (even offline).
- requires no extra infrastructure to get started
- requires no git expertise
Users are only expected to maintain their (non-SIMP) Puppetfile (if necessary), and deploy RPM-delivered updates with r10k puppetfile install.
6.4.0+: Local Puppet admins may create new Puppet environments, however: a Secondary environment is required to exist for each Puppet environment.
- The secondary environment for
productionwas generated automatically duringsimp config's initial auto-deploy in Stage B2 - New environments can be generated using the proposed command,
simp environment new. - New environments can also be cloned or symlinked from an existing SIMP extra environment (associated secondary + writable environments).
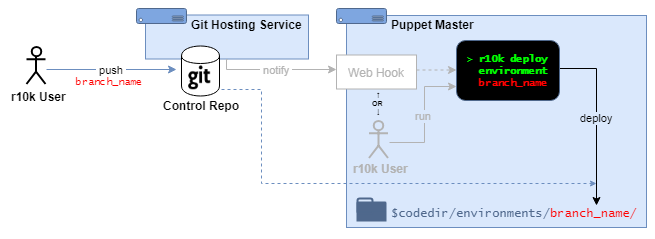
Professional: r10k + Control Repository
Puppet admins:
- maintain a Puppet control repository from an external git service.
- deploy entire Puppet environment directories (one environment for each repository branch) using
r10k deploy environment [ENVIRONMENT]- This might be done manually from the command line, or triggered automatically (e.g., from a webhook).
6.4.0+: The ISO+Puppetfile workflow will not interfere with this scenario, however a Secondary environment is required to exist for each Puppet environment.
- The secondary environment for
productionwas generated automatically duringsimp config's initial auto-deploy in Stage B2, - New environments can be generated using the proposed command,
simp environment new.- New environments can also be cloned or symlinked from an existing SIMP extra environment (associated secondary + writable environments).
- The
simp environment newcommand can be configured to run after each deployment via thepostrunsetting inr10k.yaml.
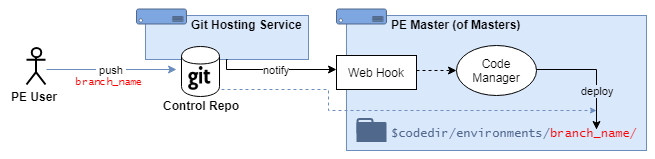
Enterprise: PE Code Manager + Control Repository
Puppet admins:
- maintain a Puppet control repository from an external git service.
- deploy entire Puppet environment directories (one environment for each repository branch) using PE Code Manager.
- This is triggered automatically from a Code Manager webhook.
6.4.0+: The ISO+Puppetfile workflow will not interfere with this scenario, however a Secondary environment is required to exist for each Puppet environment.
- The secondary environment for
productionwas generated automatically duringsimp config's initial auto-deploy in Stage B2, - New environments can be generated or cloned using the proposed command,
simp environment new.- can be configured to run after each environment deployment by setting
postrunin Code Manager'sr10k.yaml. - It may also be configured to run from a (not created) local webhook using Code Manager's
post_environment_hookssetting.
- can be configured to run after each environment deployment by setting
- New environments can be generated using the proposed command,
simp environment new.- New environments can also be cloned or symlinked from an existing SIMP extra environment (associated secondary + writable environments).
- The
simp environment newcommand can be configured to run after each environment deployment by settingpostrunin Code Manager'sr10k.yaml. - It may also be configured to run from a local webhook (not included) using Code Manager's
post_environment_hookssetting.
Options considered
| Option 1: | Option 2: | |
|---|---|---|
| Description |
| |
| Pros and cons |
|
|
| Estimated cost | MEDIUM | MEDIUM |
Action items
Outcome
(Working assumption for Sprint 82 as of 14 Mar 2019): Option 1
Resources
- (Source for https://draw.io diagrams: simp_iso_puppet_workflow_diagrams.xml)
-40,000%20ft%20overview_A.png?version=1&modificationDate=1553530307598&cacheVersion=1&api=v2)
-40,000%20ft%20overview_B%20(1).png?version=2&modificationDate=1553542989412&cacheVersion=1&api=v2)
-40,000%20ft%20overview_C.png?version=1&modificationDate=1553530413332&cacheVersion=1&api=v2)